Key Topics : Op-Amp Stethoscope, DIY Stethoscope, Heat Beat Monitor using Op-Amp, Non Inverting Amplifier, Dual Power Supply
We will see how can we make a simple Audio amplifier which can even let us hear own own heartbeat. It is important to know that this is not a power amplifier which can drive large woofers but only a small headphone, This circuit is designed not only to listen to heartbeat only, it can amplify any small sound to a level we can listen through a small speaker/ headphone.
Theory used in this circuit is the famous non inverting amplifier in Op-Amps.
 |
| Non-Inverting Amplifier basics |
The use of capacitor is to filter the DC offset and allow only the signal to pass through. Value of the capacitor will depend on the frequency range we are going to use in this application. Also we will be using couple of preset (variable resistors) so that we can change the gain as we need in our application.
This Op-Amp requires a dual power supply. Read this article to find out how to make a dual power supply. Since this requires only few milli amps I've selected the cheapest and easiest way to bias the Op-Amp. (Note that this is not suitable for circuits with higher current requirements)
 |
| Simple and cheap way to make a dual power supply. |
Lets see the Op-Amp circuit,
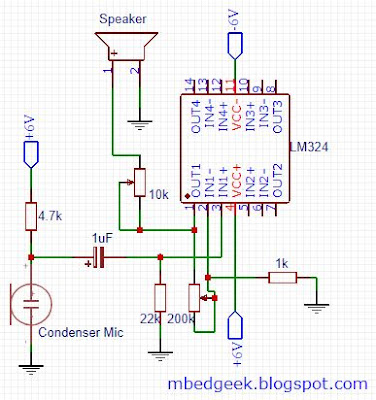 |
| Op-Amp Stethoscope circuit |
I've used LM324 Op-Amp as this is a very cheap one and capable of operating in the required voltage range. Condenser microphone is also very cheap and can buy from any electronic component store. I've used an old earphone to observe the sound. Since input side of this circuit is very susceptible to noise, I've soldered this using a perfboard to avoid loose connections compared to a breadboard.
 |
| Op-Amp Stethoscope |
Good Luck 😉